NDPluginCodec
- author:
Bruno Martins, Facility for Rare Isotope Beams and Mark Rivers, University of Chicago
Overview
NDPluginCodec is a tool for compressing and decomppressing NDArray data
according to a user selectable codec. Compression information is stored
in the codec and compressionSize fields of the NDArray.
Compressed NDArray Semantics
The new NDArray field codec is used to indicate if an NDArray holds
compressed or uncompressed data.
Uncompressed NDArrays
codecis empty (codec.empty()==true).compressedSizeis equal todataSize.
Compressed NDArrays
codec.nameholds the name of the codec that was used to compress the data. This plugin currently supports four codecs: “jpeg”, “blosc”, “lz4”, and “bzlz4”.compressedSizeholds the length of the compressed data inpData.dataSizeholds the length of the allocatedpDatabuffer, as usual.pDataholds the compressed data asunsigned char.dataTypeholds the data type of the uncompressed data. This will be used for decompression.
Compression
To compress the data, the Mode parameter must be set to Compress. Also, the parameter Compressor must be set to something other than None. After the compression is done, the CompFactor parameter will be updated with the compression factor achieved. CompFactor is calculated according to the following formula:
dataSize/compressedSize
Currently, five choices are available for the Compressor parameter:
None: No compression will be performed. The NDArray will be passed forward as-is.
JPEG: The compression will be performed according to the JPEG format.
pDatawill contain a full, valid JPEG file in memory after the compression is done. JPEG compression is limited to unsigned 8-bit data (UInt8). It is also limited to ColorMode=Mono or RGB1. For Mono the input data is 2-D (NX, NY). For RGB1 it is 3-D [3, NX, NY]. JPEG compression is controlled with the following parameters:JPEGQuality: The image quality to be used for the compression. The quality value must be between 1 and 100, with 100 meaning best quality (and worst compression factor).
Blosc: The compression will be performed according to the Blosc format. The compression is controlled via the following parameters:
BloscCompressor: which compression algorithm to use. Available choices: BloscLZ, LZ4, LZ4HC, Snappy, ZLIB and ZSTD.
BloscCLevel: the compression level for the selected algorithm.
BloscShuffle: controls whether data will be shuffled before compression. Choices are None, Byte, and Bit.
BloscNumThreads: controls how many threads will be used by the Blosc compressor to improve performance.
LZ4: The compression will be performed according to the LZ4 format. This is similar to the Blosc compressor with BloscShuffle=None but uses the native LZ4 library, rather than Blosc. It is one of the compressors used on the ZeroMQ socket interface on the Eiger detector from Dectris. NDPluginCodec can thus be used to decompress this data.
BSLZ4: The compression will be performed according to the Bitshuffle/LZ4 format. This is similar to the Blosc compressor with BloscShuffle=Bit but uses the native LZ4 library, rather than Blosc. It is one of the compressors used on the ZeroMQ socket interface on the Eiger detector from Dectris. NDPluginCodec can thus be used to decompress this data.
Note that BloscNumThreads controls the number of threads created from a single NDPluginCodec thread. The performance of all the compressors can also be increased by running multiple NDPluginCodec threads within a single plugin instance. This is controlled with the NumThreads record, as for most other plugins.
It is important to note that plugins downstream of NDCodec that are
receiving compressed NDArrays must have been constructed with
NDPluginDriver’s compressionAware=true, otherwise compressed arrays
will be dropped by them at runtime. Currently only NDPluginCodec,
NDPluginPva, and NDFileHDF5 are able to handle compressed NDArrays.
Decompression
If Mode is set to Decompress, decompression happens automatically and transparently if the codec is supported. No other parameter needs to be set for the decompression to work.
Parameters
NDPluginCodec inherits from NDPluginDriver. The NDPluginCodec class documentation describes this class in detail.
NDPluginCodec defines the following parameters. It also implements all of the standard plugin parameters from NDPluginDriver. The EPICS database NDCodec.template provides access to these parameters, listed in the following table.
Parameter Definitions in NDPluginCodec.h and EPICS Record Definitions in NDCodec.template |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Parameter index variable |
asyn interface |
Access |
Description |
drvInfo string |
EPICS record name |
EPICS record type |
NDCodecMode |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
The plugin mode (NDCodecMode_t). |
MODE |
$(P)$(R)Mode, $(P)$(R)Mode_RBV |
mbbo, mbbi |
NDCodecCompressor |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
Which compressor to use (NDCodecCompressor_t). Choices are: |
COMPRESSOR |
$(P)$(R)Compressor, $(P)$(R)Compressor_RBV |
mbbo, mbbi |
NDCodecCompFactor |
asynFloat64 |
r/w |
Compression factor. |
COMP_FACTOR |
$(P)$(R)CompFactor_RBV |
ai |
Parameters for the JPEG Compressor |
||||||
NDCodecJPEGQuality |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
JPEG compression quality, 1-100. |
JPEG_QUALITY |
$(P)$(R)JPEGQuality, $(P)$(R)JPEGQuality_RBV |
longout, longin |
Parameters for the Blosc Compressor |
||||||
NDCodecBloscCompressor |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
Which Blosc compressor to use (NDCodecBloscComp_t). Choices are: |
BLOSC_COMPRESSOR |
$(P)$(R)BloscCompressor, $(P)$(R)BloscCompressor_RBV |
mbbo, mbbi |
NDCodecBloscCLevel |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
Blosc compression level. |
BLOSC_CLEVEL |
$(P)$(R)BloscCLevel, $(P)$(R)BloscCLevel_RBV |
longout, longin |
NDCodecBloscShuffle |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
Blosc shuffle data before compression. Choices are: |
BLOSC_SHUFFLE |
$(P)$(R)BloscShuffle, $(P)$(R)BloscShuffle_RBV |
mbbo, mbbi |
NDCodecBloscNumThreads |
asynInt32 |
r/w |
Blosc number of threads for compression/decompression. |
BLOSC_NUMTHREADS |
$(P)$(R)BloscNumThreads, $(P)$(R)BloscNumThreads_RBV |
longout, longin |
Parameters for Diagnostics |
||||||
NDCodecCodecStatus |
asynInt32 |
r/o |
Status of the compression/decompression. Values are “Success”, “Warning”, and “Error”. |
CODEC_STATUS |
$(P)$(R)CodecStatus |
mbbi |
NDCodecCodecError |
asynOctet |
r/o |
Error message if CodecStatus is “Warning” or “Error”. |
CODEC_ERROR |
$(P)$(R)CodecError |
waveform |
Configuration
The NDPluginCodec plugin is created with the following command, either from C/C++ or from the EPICS IOC shell.
int NDCodecConfigure(const char *portName, int queueSize, int blockingCallbacks,
const char *NDArrayPort, int NDArrayAddr,
int maxBuffers, size_t maxMemory,
int priority, int stackSize)
For details on the meaning of the parameters to this function refer to the detailed documentation on the NDCodecConfigure function in the NDPluginCodec.cpp documentation and in the documentation for the constructor for the NDPluginCodec class.
Screen shots
The following is the MEDM screen that provides access to the parameters in NDPluginDriver.h and NDPluginCodec.h through records in NDPluginBase.template and NDCodec.template.
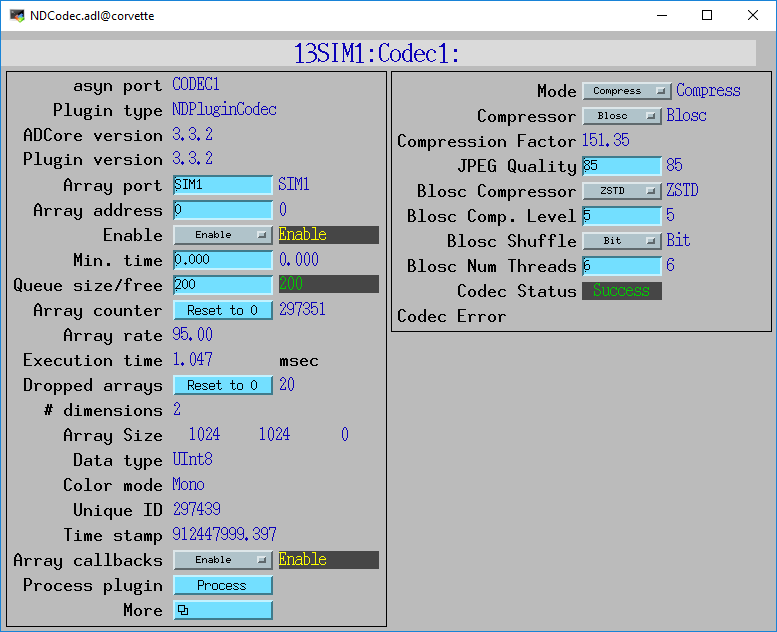
NDCodec.adl
Performance
The following screens show the performance that can be achieved with NDPluginCodec. For this test the simDetector driver was generating 1024x1024 UInt32 arrays at ~1280 arrays/s. These were compressed using Blosc LZ4 compression with Bit shuffle and 6 Blosc threads. The compression factor was ~42, so the output arrays were 98 KB, compared to the input size of 4 MB. When running with a single plugin thread (NumThreads=1) the plugin sometimes could not keep up. By increasing numThreads to 2 the plugin could always process the full 1280 arrays/s without dropping any arrays. The test was run on a 20-core Linux machine, and the simDetector IOC was using ~7 cores. NDPluginCodec was using ~6 of these. Since each array is 4 MB, this is a compression rate of ~5.0 GB/s, or about 5 times the capacity of 10 Gbit Ethernet.
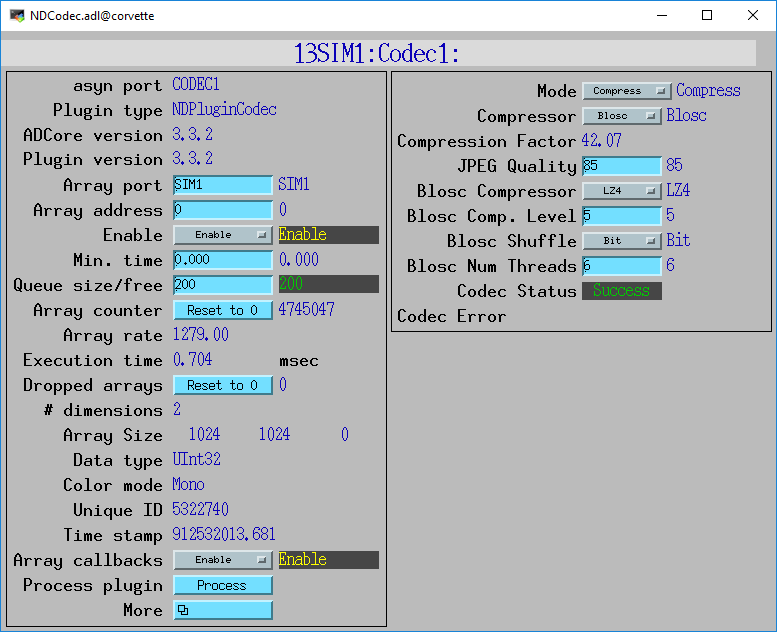
NDCodec performance with ~1280 32-bit frames/s
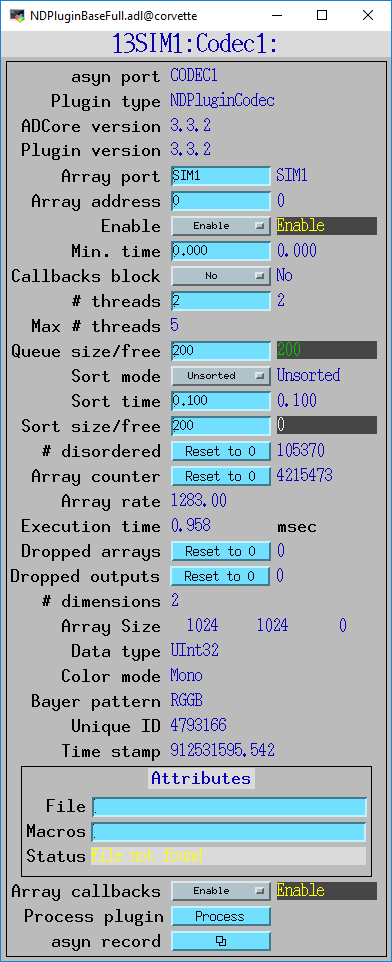
NDPluginBaseFull.adl showing that NumThreads was set to 2